Topic outline
- General
- Topic 1: Language and Linguistics
Topic 1: Language and Linguistics

Topic 1 Post Test Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 1.5 Conclusion is marked complete
- Topic 2: Phonetics
Topic 2: Phonetics
Topic 2 Pre Test
Topic 2 Post Test Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Topic 2 Pre Test is marked completeTopic 2 Post Test
Introduction to Phonetics
- Topic 3: Phonology
Topic 3: Phonology
Topic 3 Post Test Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Topic 3 Pre Test is marked completeIntroduction to Phonology
- Topic 4: Morphology
- Topic 5: Syntax
- Topic 6: Pragmatics
Topic 6: Pragmatics
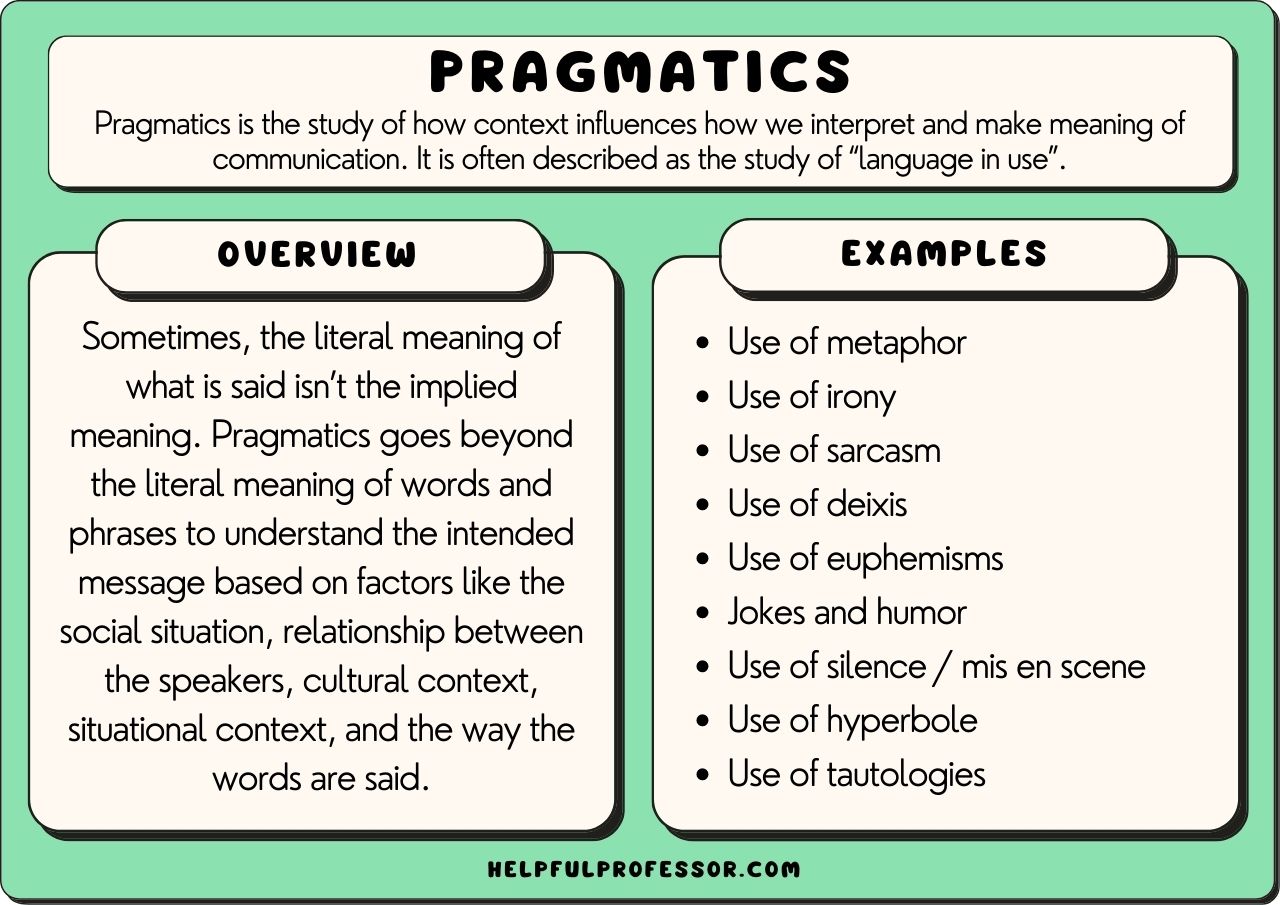
Post Test Topic 6 Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Pre Test Topic 6 is marked complete
- Topic 7 : Stylistics
Topic 7 : Stylistics
Post Test Topic 7 Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 7.1 Introduction to Stylistics is marked complete7.2 Levels of Stylistics Analysis Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 7.1 Introduction to Stylistics is marked complete7.3 Literary Devices and Foregrounding Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 7.2 Levels of Stylistics Analysis is marked complete7.4 Genres, Register and Authorial Styles Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 7.3 Literary Devices and Foregrounding is marked complete7.5 Computational and Corpus Stylistics Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 7.4 Genres, Register and Authorial Styles is marked complete7.6 Conclusion Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 7.5 Computational and Corpus Stylistics is marked complete
- Topik 8: Mid Term Exam
Topik 8: Mid Term Exam
#UTS (Evening Class) Quiz
Restricted Not available unless:- You belong to Semester 2 Evening Class
- It is before 17 May 2025, 11:55 PM
MID TERM TEST Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: You belong to Semester 2 PAGIMID TERM TEST_REMEDIAL Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: You belong to Semester 2 PAGI
- Topic 9: Semantics
Topic 9: Semantics
Post Test Topic 9 Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Pre Test Topic 9 is marked complete
- Topic 10: Systemic Functional Grammar
Topic 10: Systemic Functional Grammar
Topic 10 Post Test Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Topic 10 Pre Test is marked complete
- Topic 11: Sociolinguistics
Topic 11: Sociolinguistics
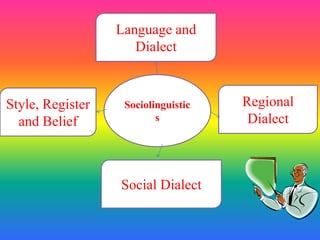
Topic 11 Post Test Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Topic 11 Pre Test is marked complete
- Topic 12: Psycholinguistics
Topic 12: Psycholinguistics

12.2 Core Components of Language Processing Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 12.1 Introduction to Psycholinguistics is marked complete12. 3 Major Sub-fields of Psycholinguistics Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 12.2 Core Components of Language Processing is marked complete12.4 Prominent Theories and Models Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 12. 3 Major Sub-fields of Psycholinguistics is marked complete12.5. Research Methodologies and Practical Applications Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 12.4 Prominent Theories and Models is marked complete12.6 Conclusion Page
Restricted Not available unless: The activity 12.4 Prominent Theories and Models is marked complete
- Topic 13: Anthropolinguistics
Topic 13: Anthropolinguistics

Post Test Topic 13 Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Pre Test Topic 13 is marked complete
- Topic 14 Discourse Analysis
- Topic 15 Ecolinguistics
Topic 15 Ecolinguistics

Post Test Topic 15 Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: The activity Pre Test Topic 15 is marked complete
- Final Test (UAS)
Final Test (UAS)

FINAL TEST SEM 2 PAGI Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: You belong to Semester 2 PAGIFINAL TEST SEM 2 EVENING Quiz
Restricted Not available unless: You belong to Semester 2 Evening Class